Aphantasia vs Hyperphantasia: Take an Aphantasia Test & Explore Your Mind's Eye Spectrum
Have you ever closed your eyes to imagine a serene beach, only to find darkness? Or perhaps when you recall a memory, it feels like you're re-watching a movie in perfect detail? The way we visualize internally varies dramatically from person to person. This internal world is a fascinating landscape, and understanding it is a journey of self-discovery. This article will guide you through the incredible aphantasia vs hyperphantasia spectrum, helping you understand your unique place within it. Have you ever wondered if the way you imagine things is different from others?
The human mind processes reality in a multitude of ways, each wonderfully unique. For some, the "mind's eye" is a blank canvas, while for others, it's a high-definition screen. Neither is better or worse—they are simply different points on a spectrum of human cognition. By exploring this range, you can gain profound insights into your learning style, memory, and creativity. Are you ready to discover your cognitive style and better understand the inner workings of your mind?
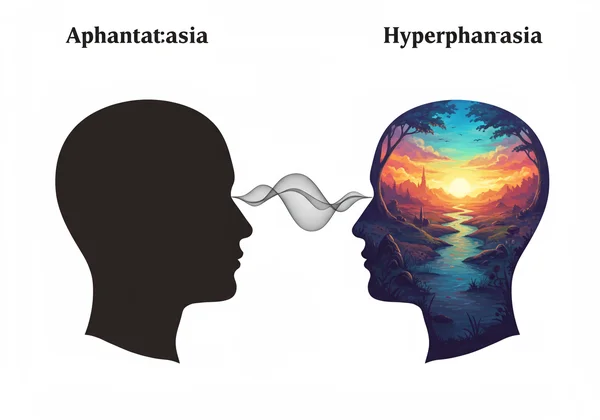
Aphantasia: Life Without a Mind's Eye
Imagine being asked to picture an apple. You know what an apple is—you know its color, shape, and taste. You can describe it perfectly. But when you try to see it in your mind, nothing appears. This experience is known as aphantasia, a condition characterized by the inability to voluntarily create mental images. It’s not a disorder, but rather a unique variation in human experience.
People with aphantasia navigate the world through concepts, facts, and semantic knowledge rather than visual memories. It's like having a vast internal database of information without a corresponding image gallery. This cognitive style affects millions, yet many live their whole lives without realizing their internal experience is different from the norm.
What is Aphantasia? Defining the Absence of Mental Images
Coined by Professor Adam Zeman in 2015, aphantasia literally means the absence of fantasy or imagination. It's often referred to as mind blindness. This doesn't mean a lack of creativity or intelligence; in fact, many aphantasics are highly successful in logical and abstract fields like programming and mathematics. Their thinking is simply non-visual.
When an aphantasic person remembers a loved one, they recall facts and feelings—the sound of their laugh, the warmth of their presence—but they may not be able to conjure their face. This conceptual understanding forms the bedrock of their mental images, which are more like data points than pictures. Understanding this is the first step toward appreciating this fascinating cognitive trait.
Common Traits & Daily Experiences for Aphantasics
Living with aphantasia shapes one's inner world in subtle yet significant ways. For instance, reading a novel with rich descriptive passages might be more about appreciating the plot and concepts than visualizing the scenes. Memory often functions differently, relying on autobiographical facts rather than episodic "replays" of events.
Some common experiences include:
- Difficulty recognizing faces, as they cannot pull up a mental picture for comparison.
- Dreaming that is often non-visual or based on concepts and emotions.
- Excelling at abstract thinking and system-based problem-solving.
- A unique sensory experience of the world, often more attuned to other senses or internal monologue.
Discovering you have aphantasia can be a revelation, explaining lifelong quirks and fostering a new sense of self-understanding. A free aphantasia test can be an excellent starting point for this exploration.
Hyperphantasia: Extremely Vivid Mental Imagery
On the opposite end of the spectrum lies hyperphantasia. If aphantasia is a blank screen, hyperphantasia is an IMAX theater in your mind. Individuals with hyperphantasia experience mental imagery that is as vivid and detailed as real life, sometimes even more so. They can manipulate these images, rotate them, zoom in, and recall memories with incredible sensory richness.
This intense vivid mental imagery allows them to design complex structures, compose music, or write stories entirely within their minds before ever putting pen to paper. Their imagination is a powerful, immersive tool that shapes their perception of reality, memory, and creativity. While it can be a source of incredible artistic inspiration, it can also be overwhelming at times, blurring the lines between thought and reality.
What is Hyperphantasia? A World of Visual Richness
Hyperphantasia is the ability to generate exceptionally strong and realistic voluntary sensory imagery. It's more than just "being a visual person"; it's about experiencing thoughts with photorealistic clarity. When someone with hyperphantasia is asked to picture an apple, they might see the glint of light on its skin, the texture of its peel, and even imagine the crisp sound of biting into it.
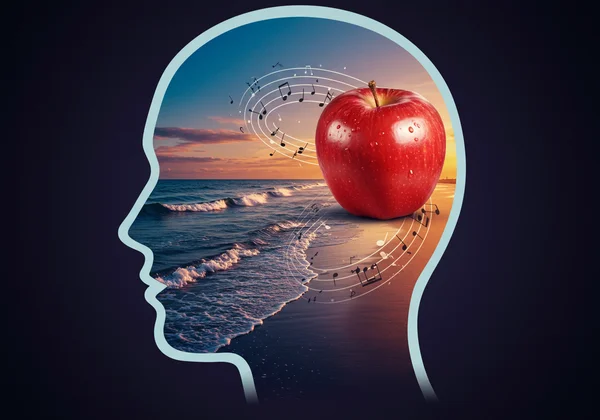

This powerful visual imagination isn't limited to sight. Many with hyperphantasia can also conjure vivid sounds, smells, tastes, and textures in their minds. Their internal world is a multi-sensory sandbox where ideas can be explored with stunning realism before being brought into the physical world.
Hyperphantasia Symptoms: How to Identify Vivid Imagination
While not a clinical diagnosis, certain traits are common among those with hyperphantasia. Recognizing these hyperphantasia symptoms can help you identify if you lean towards this end of the spectrum.
Common signs include:
- Extremely detailed and immersive daydreams.
- The ability to recall memories with photographic detail and sensory information.
- A strong emotional response to imagined scenarios.
- Often getting lost in thought, as the inner world is highly engaging.
- A natural talent for creative fields like art, design, or writing.
If this sounds like you, exploring where you fall on the visualization spectrum can unlock a deeper appreciation for your cognitive gifts. The journey starts with a simple aphantasia self-assessment.
Understanding the Full Spectrum of Visualization
It is crucial to understand that aphantasia and hyperphantasia are not binary categories. Most of the population exists somewhere on a continuous spectrum of visualization. Your ability to create mental images isn't an on/off switch but a dimmer dial, with varying degrees of clarity and control.
Many people have reasonably clear mental images but without the immersive detail of hyperphantasia. Others may only be able to conjure vague, fleeting shapes. This spectrum of cognitive diversity is a testament to the beautiful complexity of the human brain. There is no "correct" way to think or imagine; each style comes with its own unique strengths and perspectives.
From Non-Visual to Hyper-Visual: A Continuous Range
Think of visualization ability as a gradient. On one far end is total aphantasia (no imagery at all), and on the other is vivid hyperphantasia (imagery as real as seeing). In between, you'll find "hypophantasia" (dim or fuzzy imagery) and the average range of visualization most people possess.
Understanding that this is a continuous range helps de-stigmatize any particular cognitive style. It’s not about having a "good" or "bad" imagination, but about recognizing where your natural tendencies lie. This awareness empowers you to leverage your strengths, whether they are in abstract reasoning or creative visualization.
Why Exploring Your Mind's Eye Spectrum Matters
Why does this matter? Knowing your cognitive style can transform how you learn, work, and interact with the world. For a student with aphantasia, realizing that rote memorization through visual aids won't work can lead to developing more effective, concept-based study strategies. For a creative professional with hyperphantasia, understanding their powerful imagination can help them harness it more effectively.
Unlocking self-awareness is pivotal for personal growth and fulfillment. By taking the time to explore your mind's eye, you are investing in a deeper understanding of yourself. This knowledge can improve communication with others, as you can better explain your internal experience and appreciate theirs.
Discover Where You Stand: Take an Aphantasia Test
After learning about this fascinating spectrum, the natural next question is: "Where do I fit in?" The most reliable way to begin answering this is to take a structured aphantasia test. While simple thought experiments like the "apple test" are good starting points, a scientifically-inspired questionnaire provides a more nuanced assessment.
On our website, we provide a free, user-friendly aphantasia test tool to help you on this journey of discovery. Our test is designed to evaluate the vividness of your visual imagery and give you a preliminary score that helps place you on the spectrum.
The Science Behind Visual Imagery Vividness Tests
Our assessment is inspired by established psychological principles, most notably the Vividness of Visual Imagery Questionnaire (VVIQ). The VVIQ is a widely used psychological tool developed to measure individual differences in visual imagery. By asking you to rate the clarity of various imagined scenarios, a VVIQ test online can provide a standardized measure of your mind's eye.
Our test adapts these principles into a quick and accessible online format. This self-assessment provides a reliable benchmark for your visualization abilities, grounding your self-exploration in scientific methodology and offering you trustworthy insights.
Get Personalized Insights into Your Unique Cognition
Completing the initial test is just the beginning. After receiving your score, you have the unique option to unlock a personalized, AI-generated in-depth analysis. This report goes beyond a simple number, offering deeper insights into your cognitive profile, potential strengths, and challenges associated with your place on the spectrum.
This powerful tool helps you connect the dots between your test results and your real-life experiences. Are you ready to gain a comprehensive understanding of your mind? Take the free aphantasia test now and unlock the secrets of your inner world.
Explore Your Mind's Eye Today: Your Journey on the Visual Spectrum
The spectrum from aphantasia to hyperphantasia reveals the incredible diversity of human consciousness. Whether you think in vivid pictures or abstract concepts, your cognitive style is a valid and powerful way of experiencing the world. Understanding where you fall on this spectrum is an empowering step toward self-acceptance and harnessing your mind's full potential.
Your journey of cognitive exploration starts with a single step. We invite you to begin that journey today. Visit our homepage to start your self-assessment, connect with a community of fellow explorers, and embrace the unique way you see—or don't see—the world. What will you discover about your mind's eye?
Frequently Asked Questions About Visual Imagination
How to tell if you have aphantasia?
The simplest way is through self-reflection. Try to picture a friend's face or a red star. If you see nothing, you might have aphantasia. For a more structured evaluation, taking a simple aphantasia test, like the one offered on our site, can provide clearer insights by assessing your responses to various prompts.
What are hyperphantasia symptoms?
Key symptoms include having an extremely vivid, detailed, and multi-sensory imagination. People with hyperphantasia often have cinematic memories, get easily lost in elaborate daydreams, and may have a strong emotional reaction to things they imagine. Their internal world is exceptionally rich and realistic.
Is aphantasia neurodivergent?
Yes, aphantasia is widely considered a form of neurodivergent thinking. It is not a medical condition, illness, or disability, but rather a natural variation in the way a brain processes information. Recognizing it as neurodiversity helps promote acceptance and understanding of different cognitive styles.
Can you improve your visual imagination?
This is a topic of ongoing research and debate. Some individuals report modest improvements in imagery vividness through dedicated visualization exercises and mindfulness practices. However, for many, especially those with congenital aphantasia, their cognitive style is stable. The goal should be understanding and working with your natural abilities, not necessarily changing them. An online aphantasia test can give you a baseline to understand your starting point.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The test provided on this website is an educational tool for self-exploration and is not a clinical diagnosis. If you have concerns about your cognitive health, please consult a qualified healthcare professional.